Private Key JWT
This is a guide on how to create service users in ZITADEL. You can read more about users here.
Create a Service User
- Navigate to Service Users
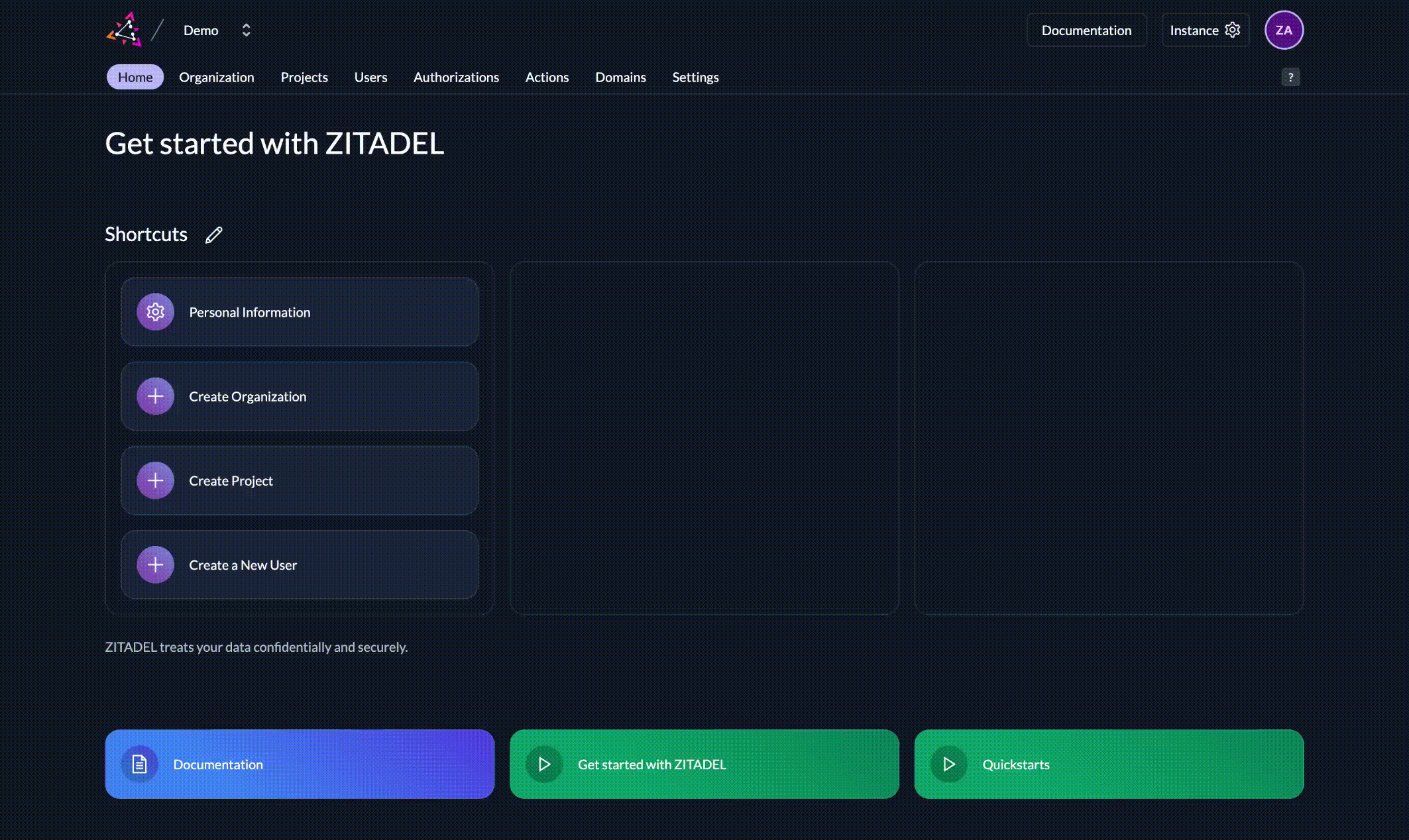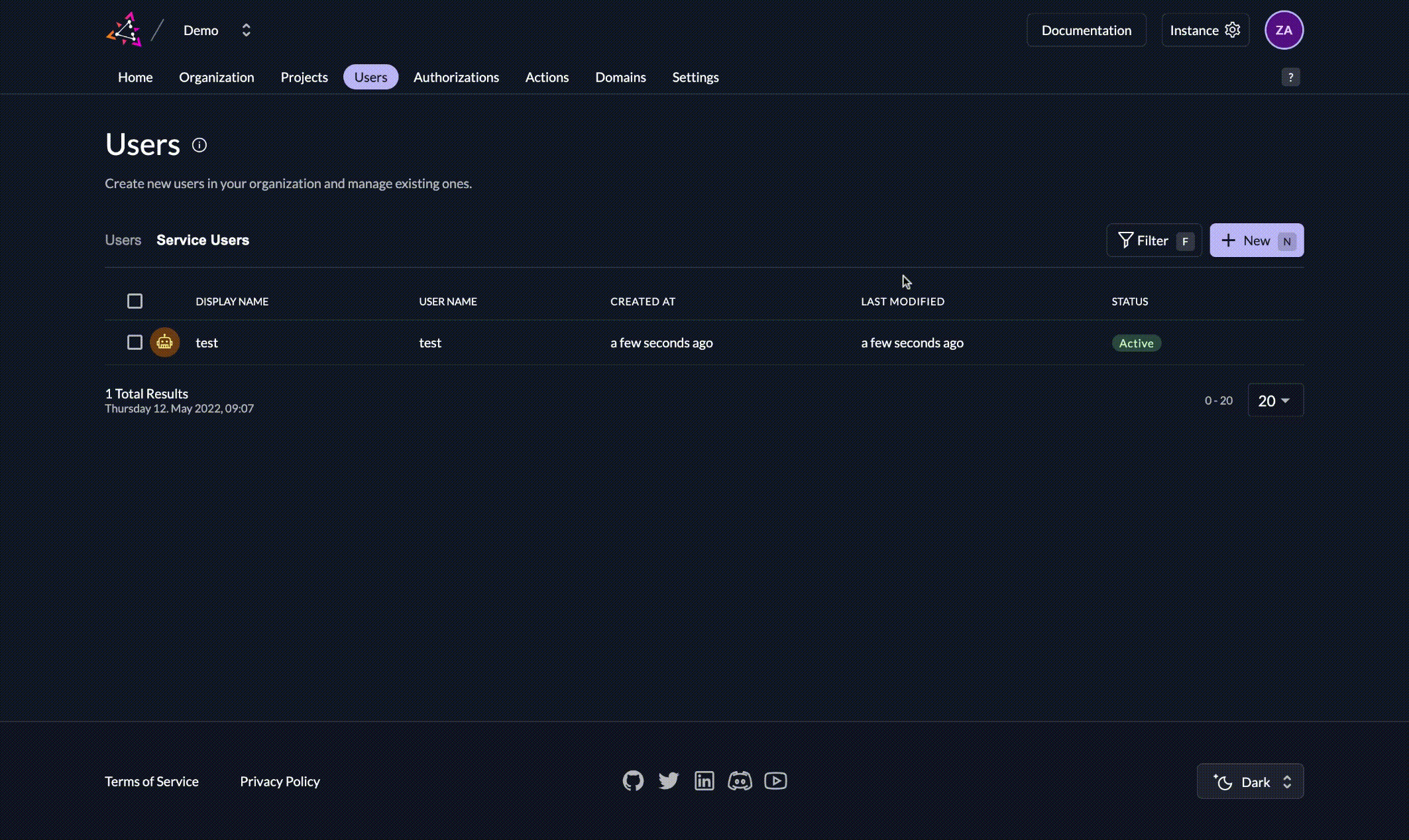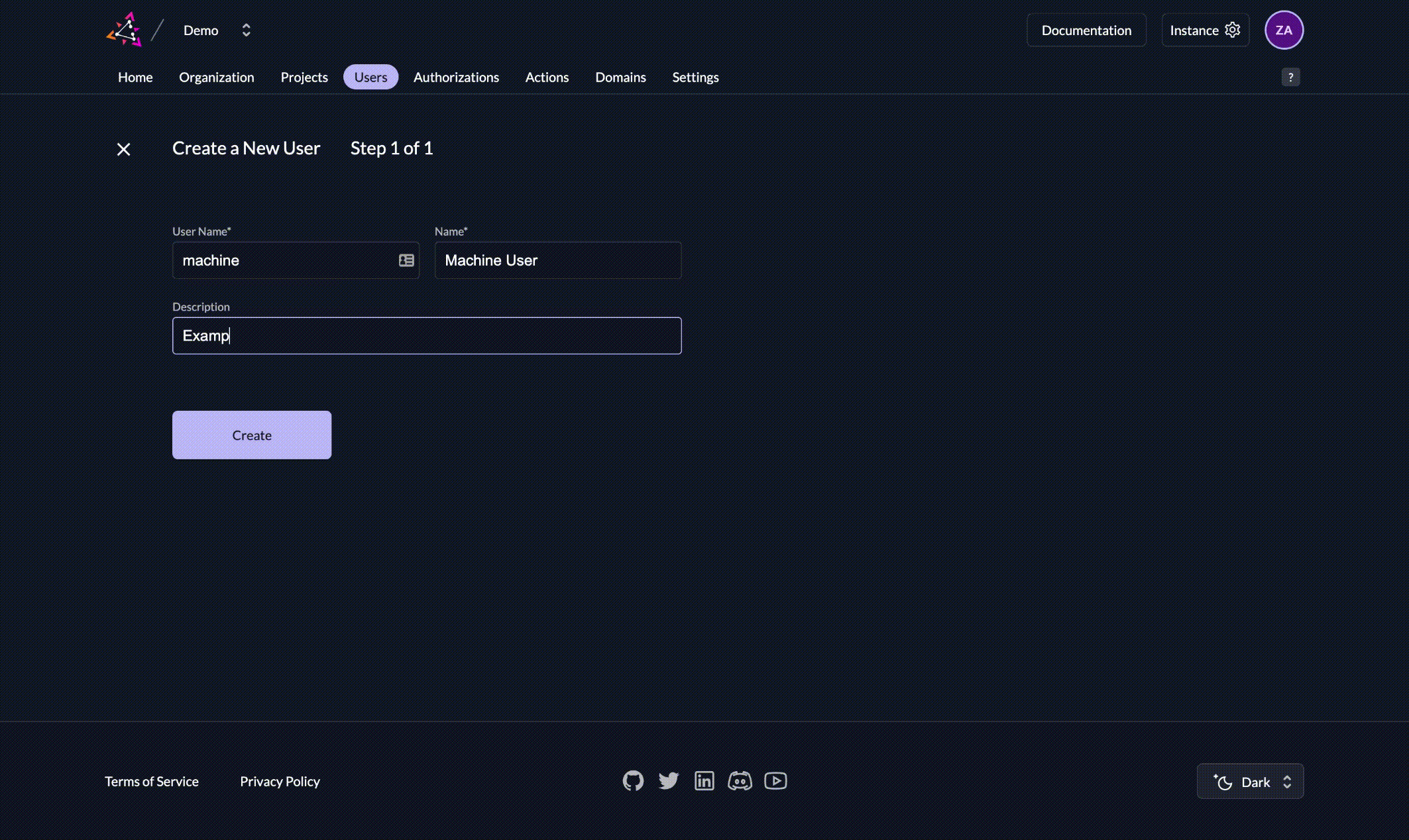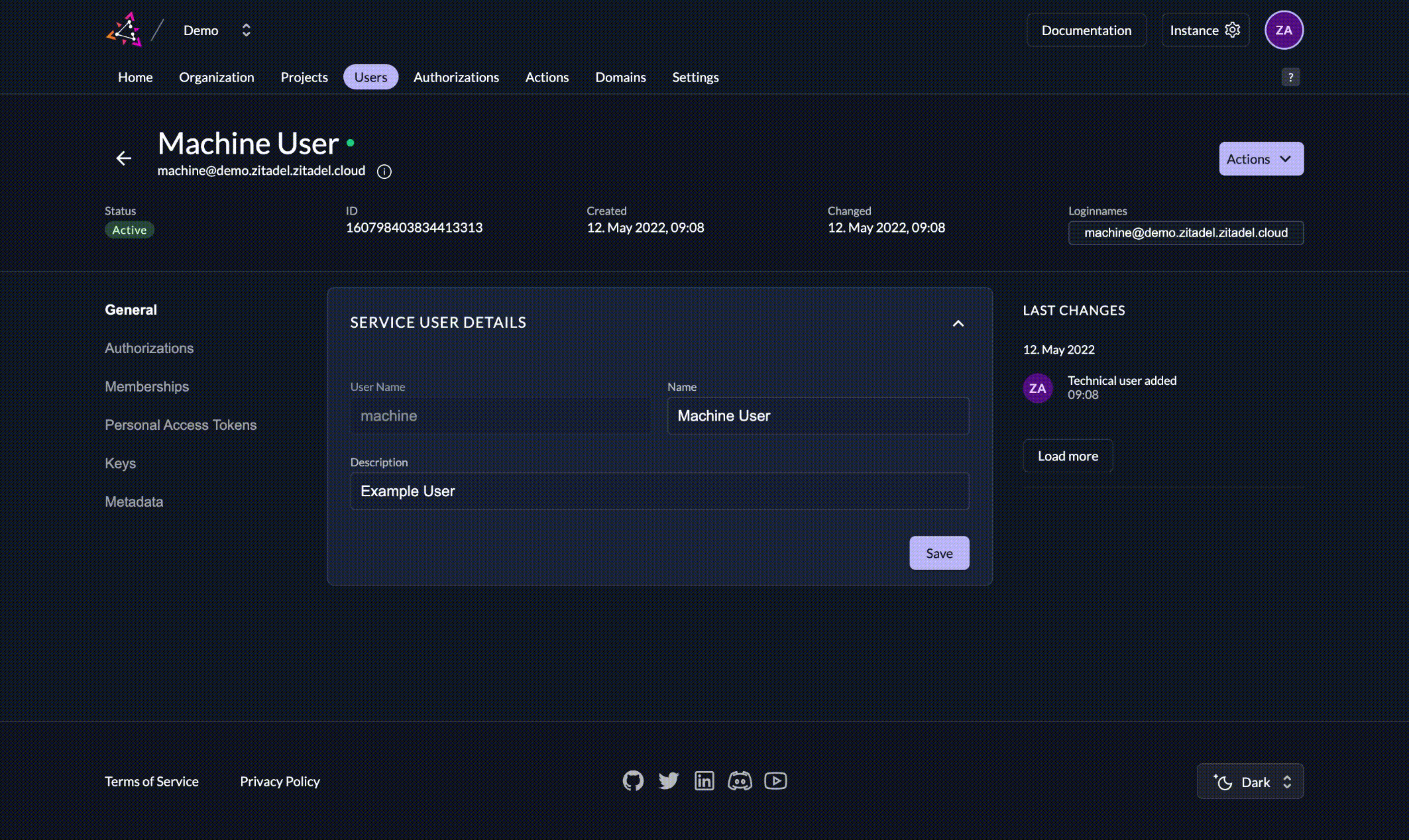
- Click on New
- Enter a user name and a display name
Authenticating a service user
In ZITADEL we use the urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer (“JWT bearer token with private key”, RFC7523) authorization grant for this non-interactive authentication.
You need to follow these steps to authenticate a service user and receive a access token:
- Generate a private-public key pair in ZITADEL
- Create a JSON Web Token (JWT) and sign with private key
- With this JWT, request an OAuth token from ZITADEL
With this token you can make subsequent requests, just like a human user.
Get an access token
In this step we will authenticate a service user and receive an access_token to use against a API.
Information: Are you stuck? Don't hesitate to reach out to us on Github Discussions or contact us privately.
1. Generate a private-public key pair in ZITADEL
Select your service user and in the section KEYS click New. Enter an expiration date and click Add. Make sure to download the json by clicking Download.
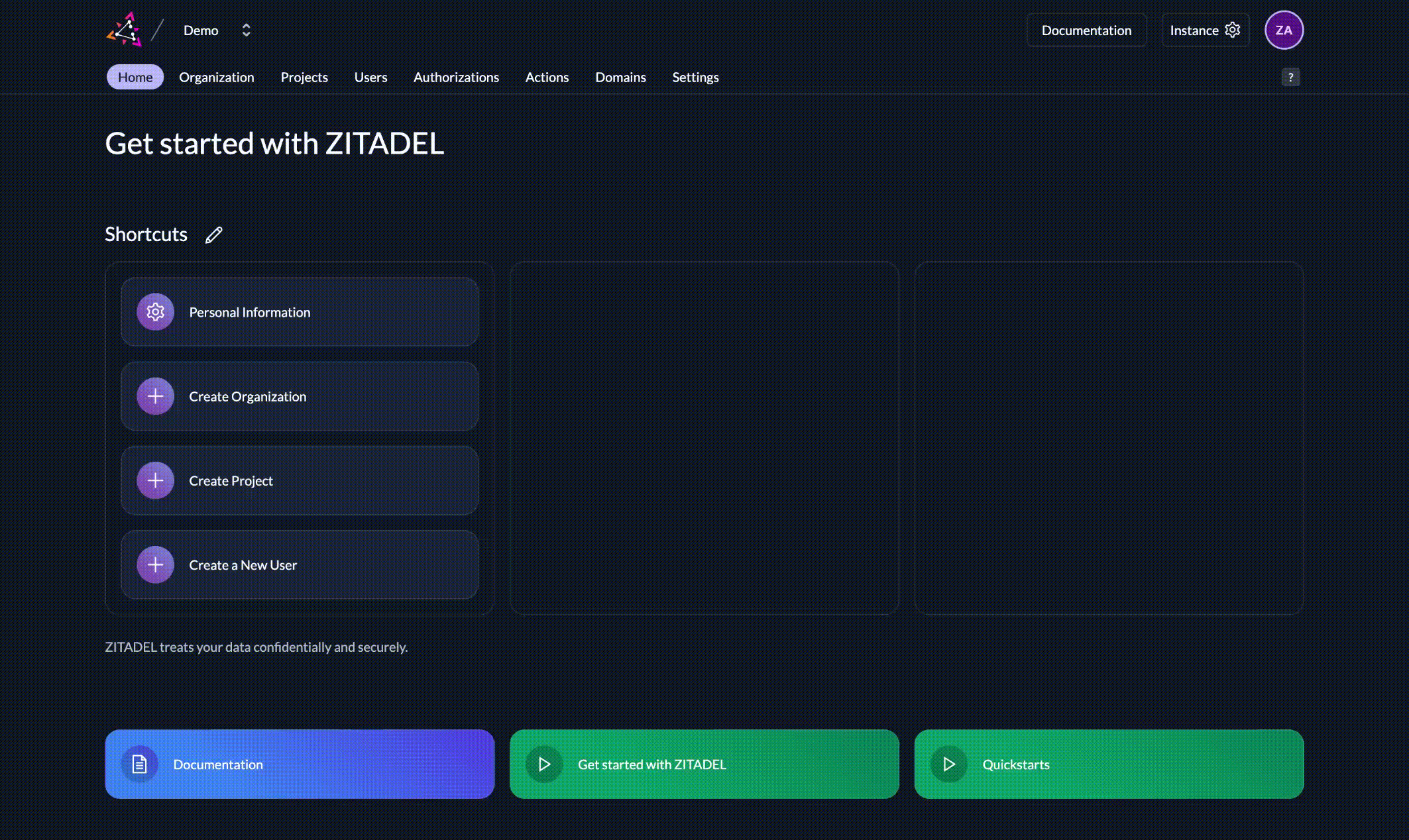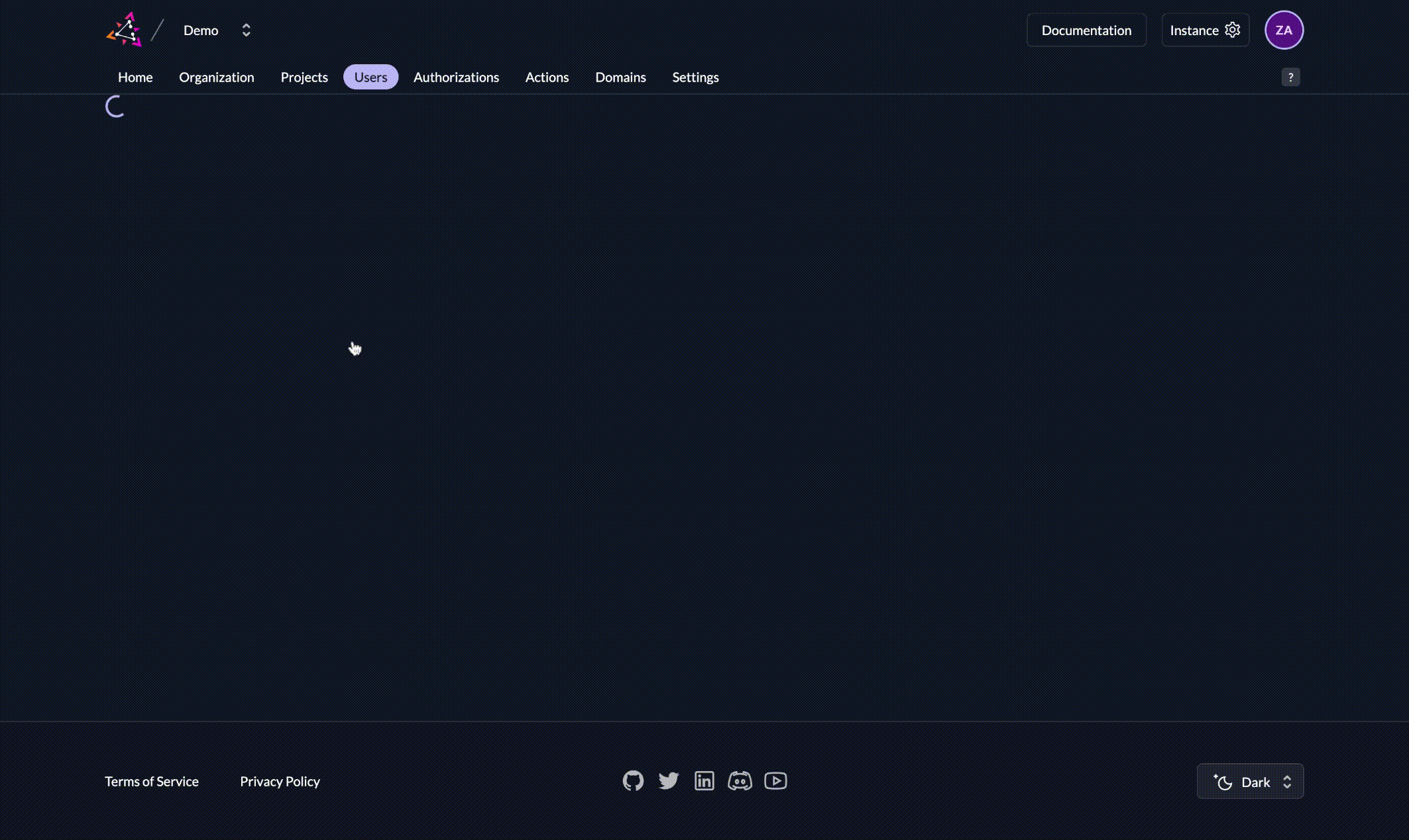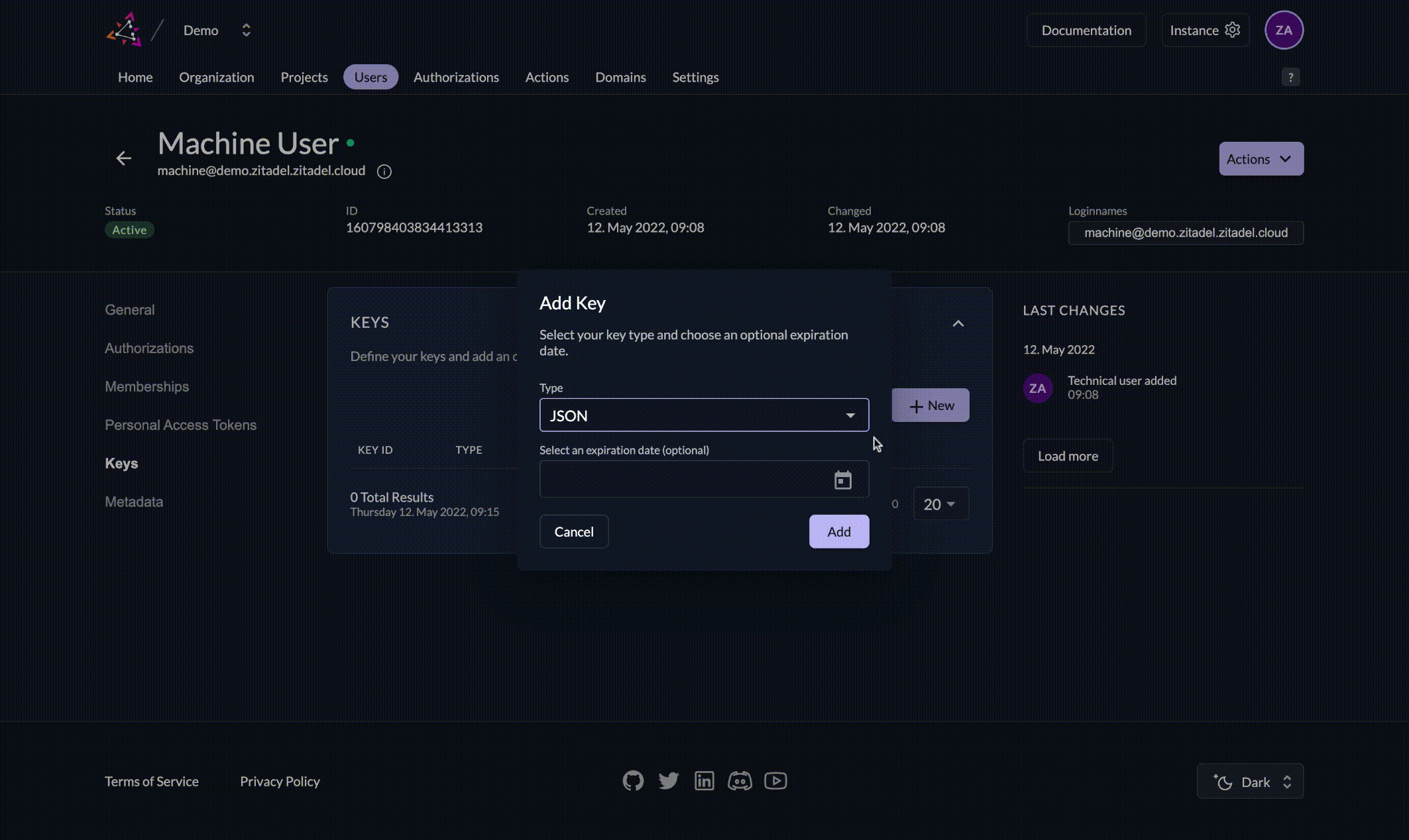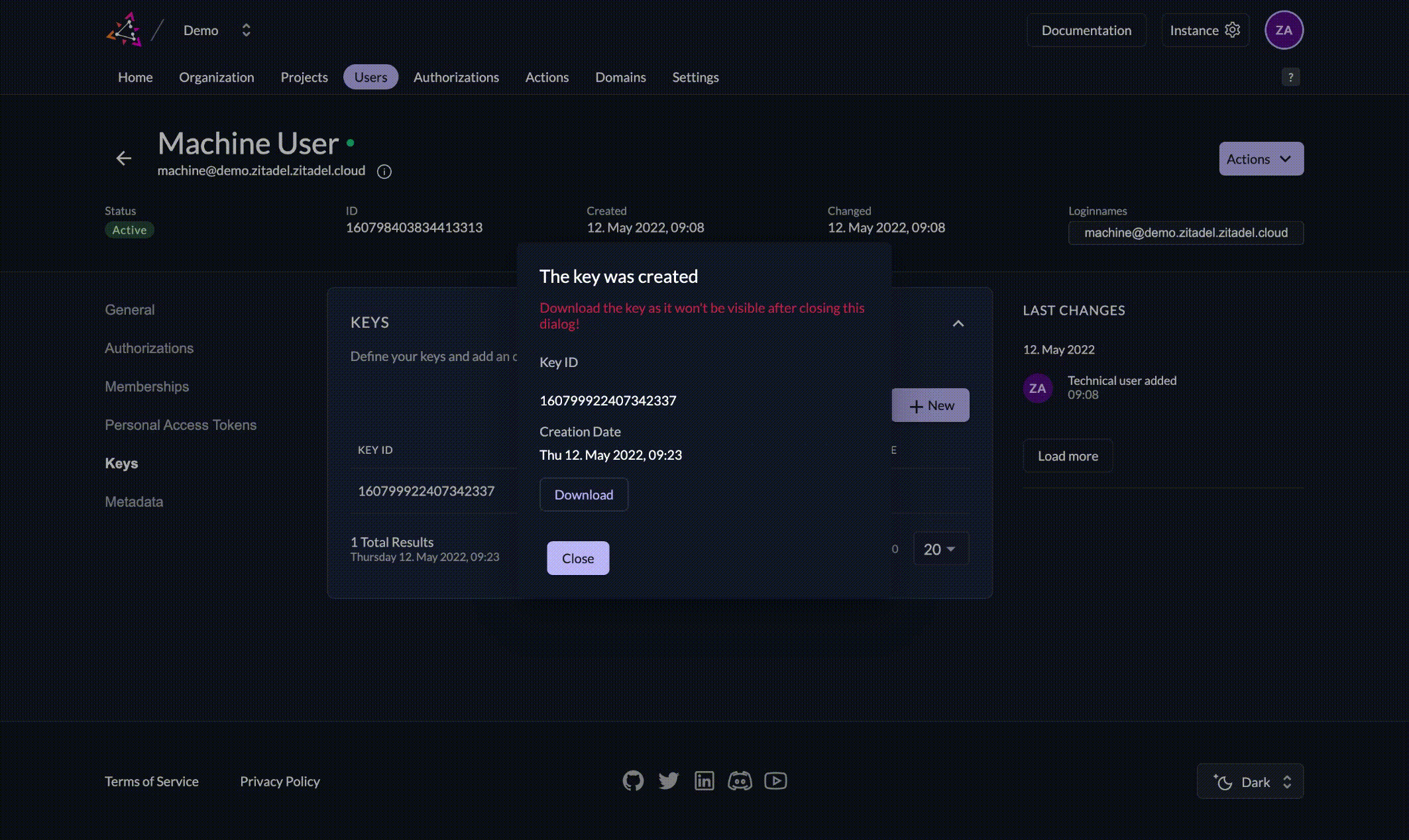
The downloaded json should look something like outlined below. The value of key contains the private key for your service account. Please make sure to keep this key securely stored and handle with care. The public key is automatically stored in ZITADEL.
{
"type":"serviceaccount",
"keyId":"100509901696068329",
"key":"-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- [...] -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"userId":"100507859606888466"
}
2. Create a JWT and sign with private key
You need to create a JWT with the following header and payload and sign it with the RS256 algorithm.
Header
{
"alg": "RS256",
"kid":"100509901696068329"
}
Make sure to include kid in the header with the value of keyId from the downloaded JSON.
Payload
{
"iss": "100507859606888466",
"sub": "100507859606888466",
"aud": "https://{your_domain}.zitadel.cloud",
"iat": [Current UTC timestamp, e.g. 1605179982, max. 1 hour ago],
"exp": [UTC timestamp, e.g. 1605183582]
}
issrepresents the requesting party, i.e. the owner of the private key. In this case the value ofuserIdfrom the downloaded JSON.subrepresents the application. Set the value also to the value ofuserIdaudmust be ZITADEL's issuing domainiatis a unix timestamp of the creation signing time of the JWT, e.g. now and must not be older than 1 hour agoexpis the unix timestamp of expiry of this assertion
Please refer to JWT_with_Private_Key in the documentation for further information.
If you use Go, you might want to use the provided tool to generate a JWT from the downloaded json. There are many libraries to generate and sign JWT.
3. With this JWT, request an OAuth token from ZITADEL
With the encoded JWT from the prior step, you will need to craft a POST request to ZITADEL's token endpoint:
curl --request POST \
--url https://{your_domain}.zitadel.cloud/oauth/v2/token \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer \
--data scope='openid profile email' \
--data assertion=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiL...
grant_typeshould be set tourn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearerscopeshould contain any Scopes you want to include, but must includeopenid. For this example, please includeprofileandemailassertionis the encoded value of the JWT that was signed with your private key from the prior step
You should receive a successful response with access_token, token_type and time to expiry in seconds as expires_in.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"access_token": "MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 43199
}
4. Verify that you have a valid access token
For this example let's call the userinfo endpoint to verify that our access token works.
curl --request POST \
--url https://{your_domain}.zitadel.cloud/oidc/v1/userinfo \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer MtjHodGy4zxKylDOhg6kW90WeEQs2q...'
You should receive a response with your service user's information.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "MyServiceUser",
"preferred_username": "service_user@{your_domain}.zitadel.cloud",
"updated_at": 1616417938
}
Summary
- With service users you can secure machine-to-machine communication
- Because there is no interactive logon, you need to use a JWT signed with your private key to authorize the user
- After successful authorization you can use an access token like for human users
Where to go from here:
- Management API
- Securing backend API